We do shipping of our products WORLDWIDE.
ALL OUR PRODUCTS ARE PACKED BY VISUALLY HANDICAPPED
100% NATURAL PLANT SCENT ESSENTIAL OILS

Ku Shen (sophora flavescens) is a root with powerful effects on cancer, metabolic diseases, neurological disorders and more.
In this post, we will discuss the benefits of Ku Shen, its caveats, and where to buy Ku Shen.
Sophora flavescens (Ku Shen, Ku Shen, Ku-Shen, Kujin, shrubby sophora) is a commonly used root in Traditional Chinese Medicine. (TCM).
This post is a little more general, as I have done extensive posts on some specific alkaloids of Kushen (see below).
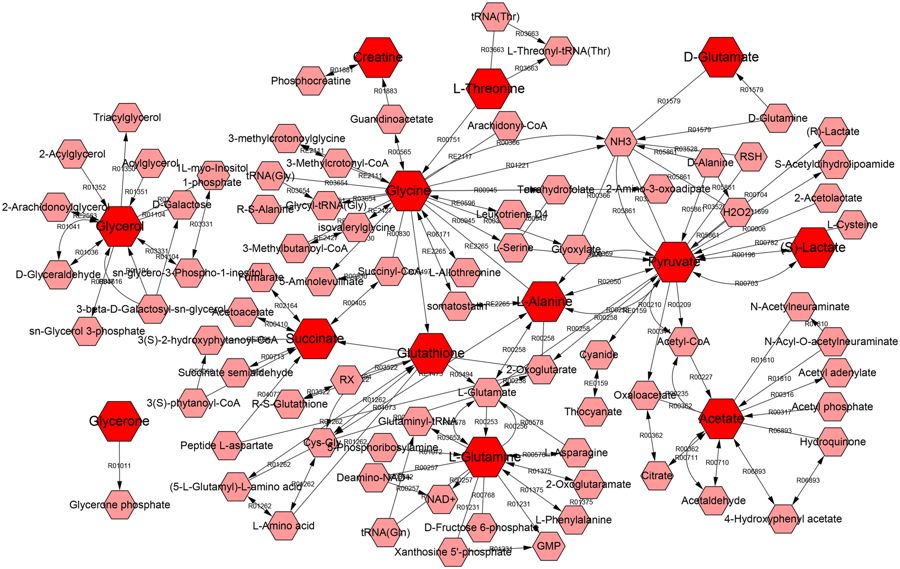
Kushen contains:

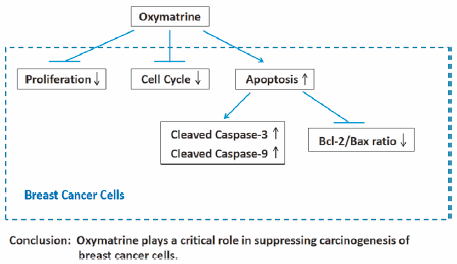
Ku shen is a powerful multipurpose anti-cancer therapeutic agent that is strong alone at fighting cancer and can synergize with other chemo-therapies.
For example, the main chemical from Kushen have been approved by Chinese FDA (CFDA) in 1995 as an anti-cancer drug to treat non-small cell lung cancer and liver cancer in combination with other anticancer drugs. R
Kushen has been used for:
Ku shen can also help with cisplatin resistant cancers.
Ku shen can reduce pain symptoms associated with cancer, such as leukopenia and nausea. R
Ku shen can help reduce neuropathic pain (via NMDA). R R

Ku shen can help with wound healing by increasing mRNA levels of growth factors such as IGF-1 and KGF in skin.
Ku shen also helps with wound healing by pro-inflammatory cytokines such as PGE2 and IL-8.
Ku shen may also help with dermatitis. R
Ku shen is commonly blended Scutellaria Baicalensis, Rheum tanguticum, Dictamnus dasycarpus, Phellodendron chinense, and Kochia scoparia and used to treat skin inflammation. R
Also, Ku shen can reduce melanin synthesis and may help improve skin whitening (via reduction of tyrosinase). R
Ku shen is a potent and selective inhibitor of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP)-specific phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) , PDE4, and PDE3, thus making it useful for erectile dysfunction and overall vascular inflammation. R
For example, ku shen can combat atherosclerosis, a disease characterized by chronic vascular inflammation. R
Ku shen helps with blood flow and blood pressure by relaxing vascular smooth muscle (via NO-sGC-cGMP signaling). R
By regulating abnormal calcium-induced rhythms in the heart, Ku Shen can improve heart failure. R R
Ku Shen can also be therapeutic for septic shock‑induced heart injury. R
Ku Shen may be beneficial for metabolic diseases as it can activate peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors gamma and alpha (PPAR-gamma and PPAR alpha, respectively). R
For example, it can help with diabetes by reducing sodium-glucose linked transporter (SGLT) activity, thus helping remove excess glucose (hyperglycemia) through the kidneys. R R
Ku shen can also act as inhibitors of a-glucosidase and b amylase, thus helping with glucose levels after eating starchy foods. R R
Ku shen can also help with diabetes as it improves oral glucose tolerance, increases serum high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) and reduces body weight, blood glucose levels and other related blood-lipid indexes (via increasing AMPK and GLUT4). R
Ku Shen has antibacterial against:
Ku shen has antiviral against:
Ku shen also has properties to combat Flavi viruses (including Zika, Dengue and Hepatitis C virus). R
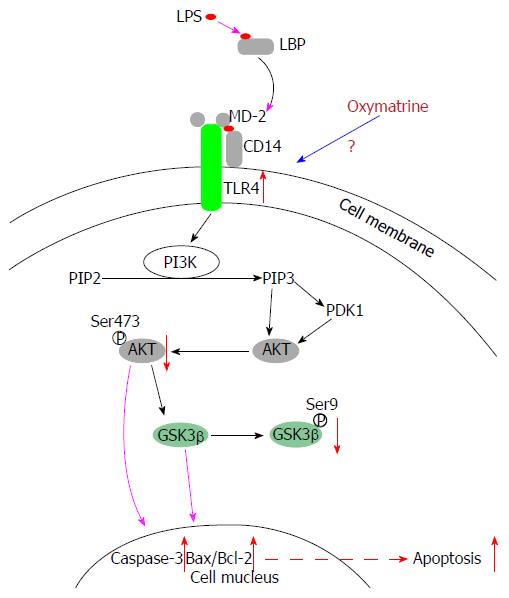
Polysaccharides in Ku shen can protect the liver from HBV and liver cancer. R
Ku shen helps with chronic hepatitis B (CHB) by acting on ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase binding protein (UQCRB) R
Ku shen can also prevent liver failure (via TLR4/PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β suppression). R
By inhibitiing epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and Y‑box binding protein 1 (YB‑1) in the liver, ku shen can prevent fibrosis of the liver. R R
Ku shen acts on gamma -aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptors and may be a therapeutic alternative to benzodiazepines. R
Ku shen may help with motor function and axon repair after spinal cord injuries (SCI). R
For example in animals, consecutive oral administrations of ku shenextract to SCI mice for 31 days increased the density of 5-HT-positive axons at the lesion site and improved the motor function. R
Maackiain in Ku Shen has antiallergic compounds that inhibit the upregulation of histamine H1 receptor (H1R) and interleukin (IL)-4 gene expression (inhibits inhibition of PKCδ activation).
Maackiain can also suppress H1R by heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90).
Ku Shen is also able to inhibit histamine release (via FAT10-NF-κB signaling) from mast cells.
Ku Shen can help with an overactive bladder (relaxes acetylcholine-induced contraction and decreases the micturition frequency by potentiating BKCa channels).
Ku Shen can combat neuroinflammation from lipopolysaccharides (LPS) by inhibiting microglial activation (via HSP60-TLR4 signaling). R R
Ku Shen can also fight neuroinflammation by inhibiting inducible NO synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) signaling.
Ku Shen can be beneficial for certain bone diseases.
For example, Ku Shen can prevent post-menopause osteoporosis (PMOP) after an ovariectomy by acting on ribosomal protein S5 (RPS5).
Also, Ku Shen can prevent implant loosening through inhibiting osteoclast formation and bone resorption.
Ku Shen can combat collagen induced-arthritis (CIA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
One ways it does this is by inhibiting of inflammation and regulating of Treg/Th17.
Another way is by reducing the levels of Th1 cytokines (IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL-1β), but increasing Th2 cytokine (IL-4 and IL-10) through attenuating the NF-κB signaling in T cells.

Ku Shen is able to promote sleep by increasing serotonin (5-HT) levels in the ventrolateral preoptic nucleus (VLPO), a sleep-promoting region.
Ku Shen is also able to normalize caffeine-induced hyperactivity and promoting a shift toward non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep. R
Ku Shen can protect the hippocampus from hypoxia (loss of oxygen and glucose) via the downregulation of MAPK and regulating lactate (LDH) levels. R
By activating the transcription factor nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2) and other downstream targets (such as NQO1 and HO-1), Ku Shen can protect the body against advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and reactive oxygen species (ROS). R R
Ku shen may help with arsenic poisoning. R
For example, ku shen is able to reduce the retention of arsenic in the liver by improving the expression of Nrf2 and HO-1. R
Ku shen can suppress endotoxemia-induced inflammation. R
For example, Ku shen has shown to prevent endotoxemia (sepsis) in the heart and lungs. R R R
Ku shen may be beneifical for psoriasis as it can suppress the expression of Pan-Cytokeratin, p63 and keratin 10, thus having having anti-proliferation effect skin cells. R
In the gut, ku shen is able to ameliorate Ulcerative Colitis (UC) by preventing inflammation in the gut. R R
Ku shen is powerful at suppressing lung inflammation. R
For example, Ku shen can suppress asthmatic reactions (Tnf-a driven). R
Ku shen can also protect against mycobacterial-induced lung growths and inflammation. R
By regulating fibroblast proliferation and collagen production, ku shen has shown to reduce antibiotic-induced scarring in the lungs. R

Androgenetic alopecia (AGA) is a hair loss disorder that commonly affects middle-aged men. R
Ku shen (L-maackiain and medicarpin specifically) can promote the growth of human hair cells and may be effective for treating AGA. R
Ku shen may be able to offer radioprotection from Electromagnetic Fields (EMFs) by modulating mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways. R
Ku shen (maackiain) can Monoamine oxidase (MAO)-A and MAO-B, making ku shen a possible candidate for depression. R R
Ku shen is neuroprotective and can protect neurons against NMDA-induced neurotoxicity. R
For example, by inhibiting PDE10A, ku shen can protect against the central nervous system from glutamate‑induced oxidative stress. R
Ku shen can protect the kidneys during chemotherapy by enhancing kidney function and modulating TH17/Treg levels. R
Ku shen can also protect the kidneys from oxidative stress by hyperglycemia making it beneficial for diabetic nephropathy (DN). R
Ku shen may help treat Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) as it can improve cognitive deficits in mice by inhibiting Amyloid-Beta (AB) plaque aggregation (suppresses the Aβ/RAGE signaling pathway). R
Ku shen may be useful for treating Parkinson’s Disease (PD) as it can improve mitochondrial function (by Parkin, PINK1 and DJ-1 expression levels).
Sophora flavescens Ait. (Leguminosae) has been proposed as a new whitening agent for cosmetics, because it has a strong ability to inhibit tyrosinase, a key enzyme in the formation of melanin.
We conducted a study to determine whether ethanol extract of the roots of S. flavescens has the potential for use as a whitening cosmetic agent by investigating its underlying mechanisms of action.
To elucidate the mechanism of action of S. flavescens extract, we used DNA microarray technology. We investigated the changes in the mRNA levels of genes associated with the formation and transport of melanosomes.
We also identified the formation and transport of melanosomes with immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence analyses. Finally, the skin-whitening effect in vivo of S. flavescens extract was analyzed on human skin.
We found that S. flavescens extract strongly inhibited tyrosinase activity (IC50, 10.4 μg/mL). Results also showed that key proteins involved in the formation and transport of melanosomes were dramatically downregulated at both mRNA and protein levels in keratinocytes exposed to S. flavescens extract.
In addition, a clinical trial of a cream containing 0.05% S. flavescens extract on human skin showed it had a significant effect on skin whitening by mechanical and visual evaluation (1.14-fold).
This study provides important clues toward understanding the effects of S. flavescens extract on the formation and transport of melanosomes.
From these results, we suggest that naturally occurring S. flavescens extract might be useful as a new whitening agent in cosmetics.
Recent Comments